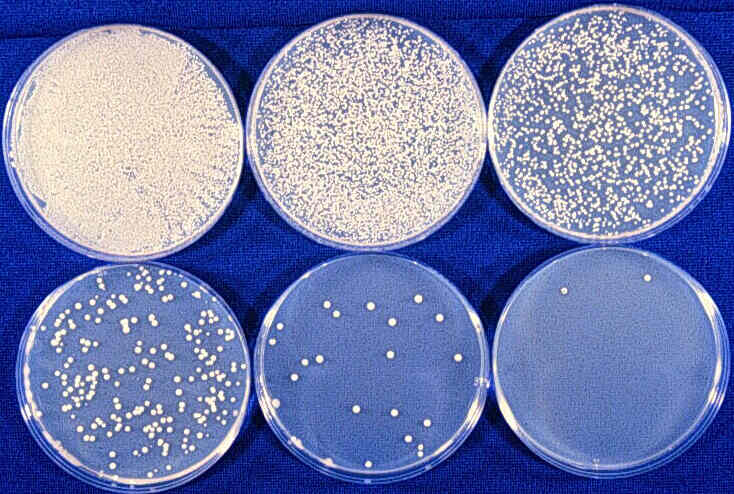
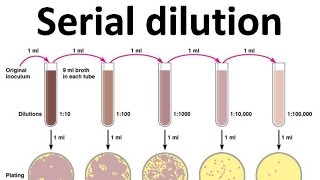
How to Know Which Plates Are Used for Serial Dilution
Spread plates Student Learning Objectives. In microbiology serial dilutions log dilutions are used to decrease a bacterial concentration to a required concentration for a specific test method or to a concentration which is easier to count when plated to an agar plate.
A 1 mL aliquot of the stock solution solution 0 is added to tube 1 which contains 9 mL of 045 saline dilent 1.
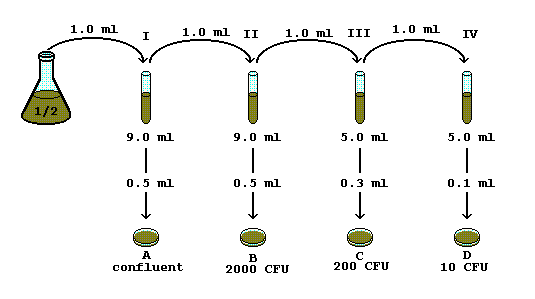
. Differentiate between a spread and pour plate. Lets assume the count might be as high as 10 6 bacteria per mL. Examples of a viable cell count are spread plates from a serial dilution of a liquid culture and pour plates.
TMTC stands for Too Many To Count Petri Plate 2 Petri Plate 3 Petri Plate 4 Number of bacterial colonies. Repeat by aliquoting 1 mL of the newly created solution 1 and adding it to tube 2. Serial dilution of a stock solution.
It is important to know what volume of the dilution you will need and the range of concentrations that you desire. As the count may be lower it would be advisable to plate the undiluted water as well as samples of the 10-1 10-2 10-3 and 10-4 dilutions. We would like the.
Aliquoting and resuspension continues in this fashion until the final tube is reached. Calculate the approximate number of bacteria using CFUs. We then isolate cultures from the colonies that grow on the agar surface.
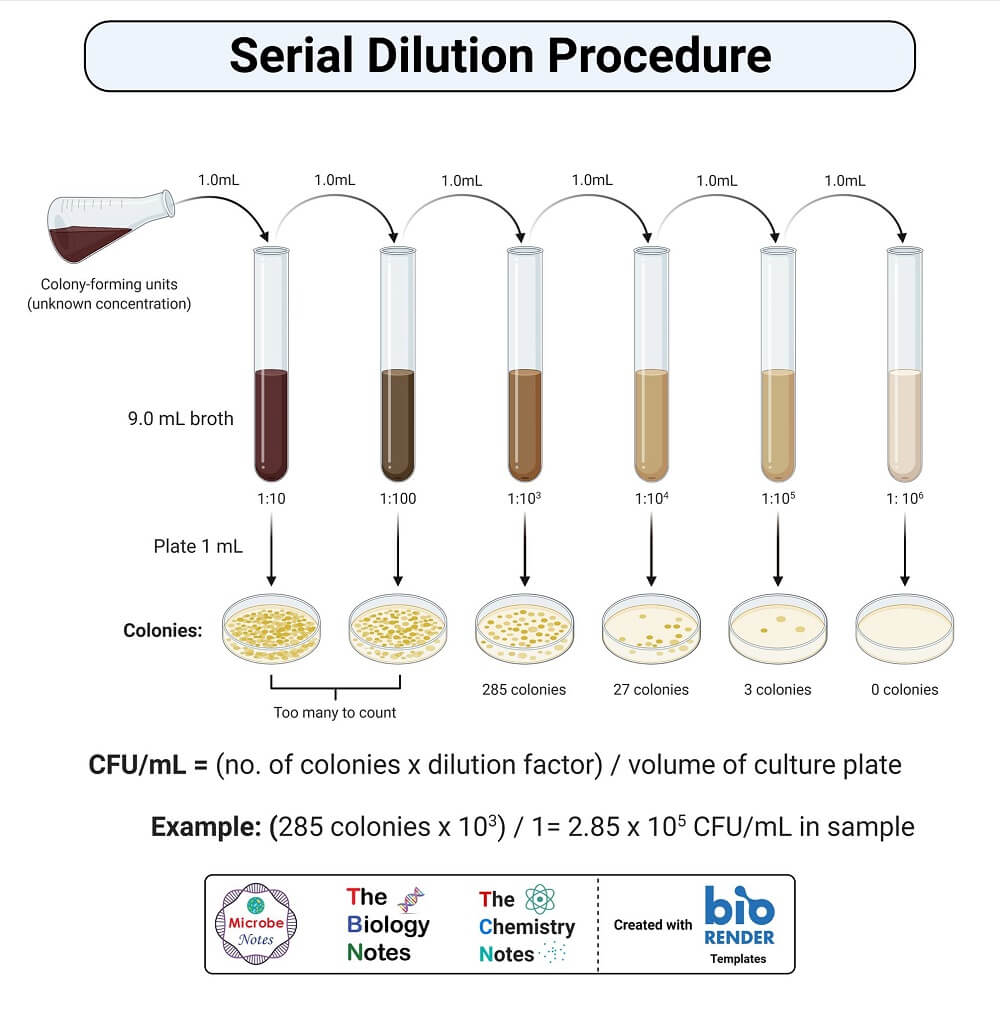
The CFUml 28 colonies 01 ml plated 280 x 107 28 x 109 CFUml 10-7 If you use these two formulae you can solve any serial. The product of this mixture is solution 1. Dilution is the process of making a solution weaker or less concentrated.
Introduction It is important in many protocols to know the number of microorganisms in a. Total dilution factor As plate E has 275 colonies in the original culture. In serial dilutions you multiply the dilution factors for each step.
1 ml added. The CFUml 275 coloniesml plated 275 x 107 28 x 109 CFUml 10-7 Plate F has 28 colonies but only 01 ml was plated. In the example below we are performing two-fold serial dilutions of a stock of analyte for use as standards.
Serial dilution involves repeatedly mixing known amounts of source culture with sterilised liquid. And to give ourselves a little wiggle room we should start at least 1 dilution before that so 110000. Please tell how and why you use the.
The dilution factor or the dilution is the initial volume divided by the final volume. Once an organism has been diluted out and allowed proper incubation time this is when one can be counted. Serial Dilution formulacalculations.
The way in which this experiment will ask you to count colonies will be by way of the naked eye. In serial dilution the selected sample is diluted through a set of standard volumes of sterile diluents such as be distilled water or 09 saline. In the beginning do 101 102 and 103 dilutions.
Differentiate between a spread and pour plate. DF V_iV_f For example if you add a 1 mL sample to 9 mL of diluent to get 10 mL of solution. A conventional way to obtain bacterial isolates from an environmental sample is to prepare a liquid suspension of the sample make serial dilutions then spread a small volume of each dilution onto one or more agar plates.
Serial dilution and pour plates Virtual Student Learning Objectives. Serial dilution involves the process of taking a sample and diluting it through a series of standard volumes of sterile diluent which can either be distilled water or 09 saline. After that a small amount of sample from each dilution is used to prepare a series of pour or spread plates.
If you prepare a 10-4 110000 dilution of the water and plate 1mL there should be 100 colonies on the plate after incubation. Understand the need for performing serial dilutions in clinical and environmental samples. 1 ml added to 9 ml gives a 10-fold dilution.
Serial dilutions can be performed in tubes microfuge or 12 X 75 mm or in the wells of plates depending on the volumes you require. Understand the need for performing serial dilutions in clinical and environmental samples. This procedure outlines how to do 10-fold serial dilutions however the volumes of buffer and phage may be adjusted for 2- 5- 100- or 1000-fold dilutions.
That would be a dilution factor of 10010000000 or 1100000. You also do serial dilutions and plate 3 dilutions to get a rough bacterial count to correlate with OD. Formulacalculations for serial dilution technique.
Dilutions should keep at 4C for a few days but experience has shown that its better to make them right before using them. Then a small measured volume of each dilution is used to make a series of pour or spread plates. After incubation count the number of bacterial colonies growing in Petri plates labeled 2 3 and 4.
With a spread plate one makes serial dilutions in liquid media and then spreads a known volume from the last tube in the dilution series. 01ml contains 001g of soil and you have 1 colony so 1g soil must have 100 colony for you to see 1 colony on. Serial dilution is a series of dilutions usually twofold or tenfold used to determine the titer or concentration of a substance in a solution.
If there are more than 200 colonies on a Petri plate stop counting and enter TMTC in the table below. Calculate the approximate number of bacteria using CFUs. Dilution IDs for 11-step 12 Serial Dilution 11 11612 1814 132 164 1128 1256 1512 11024 12048 Repeat Serial 12 Dilution Steps for Each Range Solution 5 plates required Range A Plate 1 Range B Plate 2 Range C Plate 3 Range D Plate 4 Range E Plate 5 Based on definition of plate layout and dilution values MVS grabs necessary.
Ideally therefore we would like to get 100 bacteria on the plate that we count. A serial dilution is any dilution in which the concentration decreases by the same factor in each successive step. This general microbiology practical lecture explains the serial dilution techniques in pour plate method to isolate bacteriaFor more information log on to-.
Calculation of this is a multiple of the counted number of colonies multiplied by the dilution used. Then well do three more 110 dilutions to. Introduction It is crucial in many protocols to know the number of microorganisms in.
So how many dilutions. The first plate of serial dilution 01ml of the 5g in 50ml and you have 1 colony.

An Illustration Of Single Plate Serial Dilution Spotting Sp Sds Download Scientific Diagram
Explain The Serial Dilution Process Plate Counts Biology

Serial Dilution In Microbiology Definition Formula Procedure And Calculator
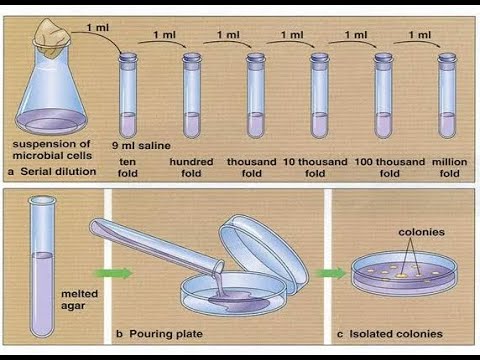
5 1 Introduction To Enumeration Of Bacteria Biology Libretexts

Serial Dilution Techniques And Requirements Iul Instruments

Serial Dilution Method Definition Procedure Application

Serial Dilution Method Purpose What Is Serial Dilution Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

A Descriptive Diagram Of A Serial Dilution Spotting Assay Used To Download Scientific Diagram
Serial Dilution Definition Formula Calculator Procedure Uses
Serial Dilution Followed By Plating Download Scientific Diagram

Serial Dilution Methods And Calculations Youtube

Why Do We Need To Serially Dilute The Culture Before Plating Quora

Serial Dilution Plate Map For 96 Well And 384 Well Plates Download Scientific Diagram

Serial Dilution Techniques And Requirements Iul Instruments
Why Is It Necessary To Dilute A Sample To Determine Bacterial Numbers Quora

Schematic Diagram Representing The Serial Dilution And Plating Process Download Scientific Diagram